In our homes and offices, we will often hear that someone is saying “plug it in the AC outlet” whenever an appliance is about to be used. When we purchase an electronic gadget, it is just common that the salesperson will tell you that it is rated 220 volts or 110 volts AC. And if you are a car owner complaining to a mechanic about the failure on the vehicle’s electrical system, you will sometimes hear the mechanic saying “the alternator is not giving off enough AC voltage”. Then what really is this alternating current or AC?
The Sine Wave
As the name implies, alternating current (AC) is a form of energy that alternates its level with respect to time. An alternator that charges up the SLI battery of your car is one concrete example of a device that generates AC voltage. It works when a magnet known as rotor rotates around a conductor wound in coils known as stator.
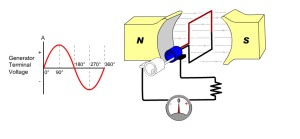
Image Source: Wisc-Online Website
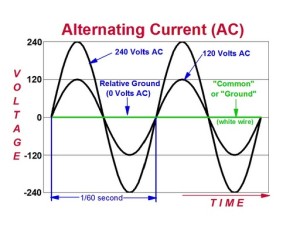
One complete rotation or cycle (equivalent to 360⁰) results to the generation of what is known as a “sine wave”. Whenever you hear the terms 60 Hertz (a unit of frequency), that means that there occurs 60 cycles of sine waves within 1 second. The amount of voltage an alternator generates typically ranges from 13.5 to 14.4 volts AC. This range of electric current will be rectified and regulated to 12 volts DC which will then be used to charge up the SLI battery.
Image Source: Emyrdiniz Website
The AC and DC Voltage
You may realize that alternating current (AC) plays an important role in our homes, on our vehicles, and in fact on almost all of the electronic gadgets we use everyday. The generators in power plants and alternators in our vehicles are where alternating current (AC) is actually produced. We know that rechargeable batteries that power our laptops and LED flashlights produce DC voltage. But remember that this DC voltage will not be available without the AC voltage coming from the AC outlets. A process known as AC to DC conversion will be covered in the next blog post.
Related articles: