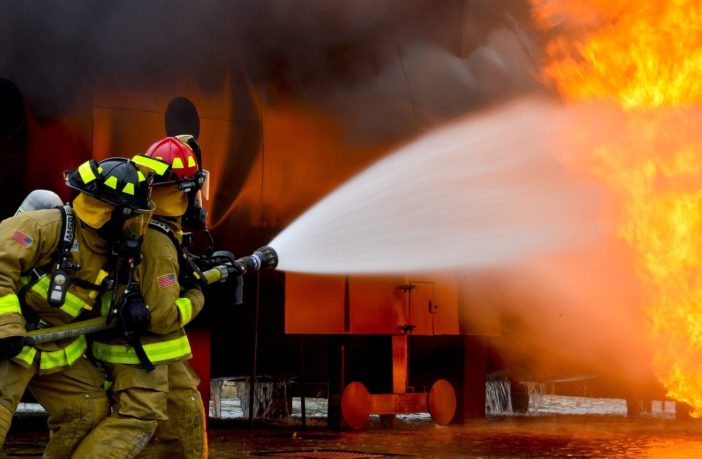
The battery market is hot, but it might be downright combustible. While batteries have revolutionized the way we generate power, they also point us to potential problems.
Overheating is a very real issue when it comes to stacking multiple units of lithium ion batteries for power generating. Racks of batteries the size of mini-apartments are installed in crammed urban spaces to allow consumers to access cheaper, renewable energy and supply backup power during outages.
Preventing Battery Fires in New York:
Yet while this cramming isn’t dangerous, it isn’t exactly safe either. Now U.S. city planners are worried that blazes may be difficult to control given the batteries’ widespread presence on building rooftops and household basements.
According to the Electric Power Research Institute, New York is reviewing the safety of these batteries, limiting their scope. At this point, there has not been a single lithium-ion installation inside a city building as New York fire department wants to ensure appropriate safety standards. Batteries can ignite, and hours or days later, reignite causing fires that no one wants to have to deal with.
Battery Boom:
Lithium-ion batteries have gotten a lot cheaper. Prices have dropped around 80% since 2010, reflecting the demand for electric cars. This has increased the demands for utilities to incorporate batteries that can store energy produced by solar and wind farms.
Massachusetts, California and New York have plans to increase the amount of storage on their grids. New York City wants 100-megawatt hours deployed by 2020. This is enough to power anywhere from 25,000 to 80,000 homes for an hour.
Lithium-ion batteries are expected to make the majority of energy storage on America’s power grid within the next decade.
Understanding the Lithium-ion Battery:
The probability of battery fires is relatively low. But to understand why they sometimes combust, it’s important to examine their technical logistics. There are two electrodes inside each lithium-ion battery. There is a positively charged cathode, and a negatively charged anode. Both are separated by a thin sheet of plastic that keeps them from touching.
When you charge a lithium-ion battery, lithium-ions are pushed by electricity from the cathode to the anode. When the battery discharges, the lithium ions flow from the anode toward the cathode. This is the reaction that powers your favourite devices.
What Causes Explosions?
When lithium ion batteries are released intermittently in trickles, they can power your device for the entire day. When they are released all at once, they can lead to explosions.
Most of the fires and explosions come down to short-circuiting. This occurs when the plastic separator fails to do its job, leading to the cathode and anode to touch. Once this happens, the battery begins to overheat.
When a Separator Fails:
Due to increased market demands, manufacturers are looking to push out their products at the highest available rates to beat competitors. This often leads to poor design and construction of battery components. Sometimes there isn’t enough space for the electrodes and the separator in the battery.
Sometimes it’s about individual practice. Batteries left in extreme heat are prone to combustion. If you drop your devices too hard, or too often, it’s likely going to cause internal disruptions.
Bad or poorly designed chargers can be detrimental. Using official chargers are recommended against cheaper, faultier ones in the market.