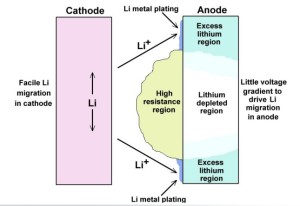
Lithium plating is the formation of metallic lithium around the anode of lithium-ion batteries during charging. Plating, also called deposition, can cause these rechargeable batteries to malfunction over time.
There are many reasons why a battery fails, the most common of which were discussed in the posts “5 Reasons for Battery Failure” and “Three Battery Problems and How to Deal with Each”. Lithium plating, however, is one of the most difficult-to-understand reasons of battery failure. In this post, we will aim to dig deeper into how such a phenomenon in the battery’s electrochemical process occurs, and how can it be avoided.
Reasons Behind Lithium Plating
During the charging process, lithium ions from the cathode are inserted into compounds with layered structures in the anode. During this process, which is called intercalation, is when lithium plating takes place. There are two main reasons for this. One is the high charge current forcing the lithium ions to move at a faster reaction rate and accumulate in the surface of the anode (usually made of carbon compounds). Another reason is charging at low temperature. In this environmental condition, the reaction rate slows down thus affecting the intercalation of lithium ions.
Lithium Plating Formation
Image Source: The Aerospace Corporation
Other reasons attributed to lithium plating are non-uniformity in cell or stack designs and other properties of the anode.
How Lithium Plating is Detected
Detecting the occurrence of lithium plating is not an easy job, especially for common battery consumers like us. But scientists are very enthusiastic to perform various tests for detecting lithium plating in Li-On batteries because of their objective to minimize (if not totally eliminate) this battery life killer. Here are the detectable indicators of lithium plating in a Li-On battery.
- Discharge voltage gradually decreases
- Increase in anode resistance
- Increase in anode overpotential
- Changes in electrolyte polarization in cell
How to Avoid Lithium Plating
The two simplest ways to avoid lithium plating is to prevent over voltage (above 4.2 volts per cell) during charging, and charging and discharging at low temperature (below 15⁰C). Scientists, however, keep on finding ways on how to combat lithium plating in coordination with different battery manufacturers.
Related Articles: