Barlow’s wheel was designed and constructed in 1822 by Peter Barlow, an English mathematician and physicist. This wheel was based on the separate discoveries of Hans Christian Oersted and Michael Faraday. It is known to be one of the earliest demonstrations of a homopolar motor – which is basically a direct current electric motor that has two magnetic poles. The term homopolar is an indication that the conductor’s electrical polarity and magnetic field poles do not change, and so no commutator is required.
The experiment that involved the creation of this apparatus aimed to show how a magnet reacts to a current and how a rotating motion is produced.
This apparatus had the following components:
- A wooden base
- A stand composed of two perpendicular sticks/rods on one side of the base with a vertical plane hanging from the horizontal pole
- A star-shaped copper wheel attached to a vertical plane (as shown in the image below)
- A permanent U-shaped magnet attached at the bottom of the wooden base
- A pool of mercury in the middle of two opposing magnet poles
- A wet battery contraption with two wires – one is connected to the vertical plane and the other immersed in the mercury pool.
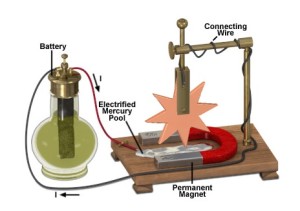
What made Barlow’s wheel move?
Basically, the interaction between the electric current and the magnet made the star shaped wheel turn. The pool of mercury was electrified through the battery and one point of the star wheel was dipped into it. When the current reached the wheel, it reacted to the magnetic field that was generated by the U-shaped magnet. It caused the wheel to turn. When the point was raised from the mercury because of the rotating motion, the circuit broke. But when the next point dipped, it restored the electrical contact.
The speed of the rotation depended on the strength of the current and magnetic field.
It has to be noted that the star-shaped wheel was not really necessary and that the Barlow’s Wheel could work with a round disk – as long as it is made of copper.