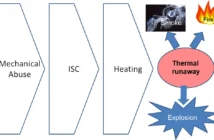
In a previous post, we discussed the advantages of using Lithium-ion Polymer batteries, popularly known as Lithium-Polymer (LiPo) batteries, over conventional ones. Lithium-Polymer batteries are widely used in personal electronics – like mobiles, tablets and laptops, radio controlled cars and electric or hybrid cars. Today we are going to discuss how these batteries are actually made in factories.
Preparing the Electrodes
Electrodes of the battery, i.e. anode and cathode are prepared separately, in different rooms. Even slight contact or mixing between the two can destroy the battery. Cathode is made of carbon while anode is made of Lithium Compounds. Cathode is covered with copper foil while anode is covered with aluminum foil. The electrodes are manufactured as long thin sheets. Watching the never-ending strips of electrodes being rolled out is a sight to behold.
After the sheets are ready, they are compressed to make them very thin. Remember that the anode and cathode are still being processed separately. The electrode sheets are then cut into required width using machines. The thin rolls of electrodes are fed into another machine that attaches a terminal to it and cuts it into required length.
Combining Electrodes
A thin semi-permeable membrane is inserted between a set of one anode and one cathode. Another machine takes this set of three layers and folds them many times to make the size compact. Finally it is wrapped up and taped and inserted into its casing to form one cell. The casing is thermally welded from three sides.
Pumping Electrolyte into the Cell
Lithium Polymer battery gets its name from the Lithium-ion polymer that is used as electrolyte. The electrolyte is pumped into the cell just prepared. This process of adding electrolyte must take place in special chambers where temperature and humidity are controlled tightly. Otherwise, the electrolyte may get spoiled and ruin the battery. Once the electrolyte is pumped in, the fourth side of the battery is also sealed.

Image Courtesy: http://learn.sparkfun.com
Charging Battery for the First Time
After the battery is ready, it has to be charged. This is called forming the battery. Charging starts at low voltage that builds up gradually. After charging is complete, the batteries are compressed strongly for a couple of hours at high temperature. Compression is done to remove any air that might have accumulated in the battery during its first charge cycle. During the compression some electrolyte might collect on the sides of the battery casing. It is removed and then the battery is trimmed.
Finishing Touches
A protective circuit is attached to the battery. The protective circuit ensures that the battery doesn’t get overcharged, remain undercharged or get short-circuited. Finally the naked battery is sent down a long hot tunnel (typically 4-foot long oven) where it gets its cylindrical heat shrink label and comes out as the AA battery that we are familiar with.
Related Posts: